The marketing world is experiencing a paradigm shift: funnel vs flywheel. Gone are the days when the traditional marketing funnel was the go-to strategy. As businesses evolve and customer needs change, companies must adapt to a new model that focuses on customer experience and generating momentum: the flywheel model.
This ultimate guide to funnel versus flywheel will take you on a journey exploring inbound methodology, comparing the differences between the funnel vs flywheel approaches, and showing how you can harness the power of the flywheel model to revolutionize your marketing strategy.
Throughout this guide, we'll explore the origins of the marketing funnel, the emergence of the flywheel model, and the key components that make it so effective. We'll also discuss how to transition your business from the funnel to the flywheel approach, implement the funnel vs flywheel model effectively, and measure its success.
Finally, we'll provide real-life examples of companies excelling with flywheel marketing. By the end, you'll be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to effectively implement the funnel vs flywheel model in your business grow your own business.
Short Summary
-
The Flywheel Model is a cyclical approach to customer satisfaction, retention and advocacy that drives business growth.
-
It involves reducing friction points in the customer journey, creating engaging content and personalizing interactions with customers.
-
Real life examples of successful flywheel marketing strategies show its potential for driving long term success.
Understanding the Modern Marketing Funnel
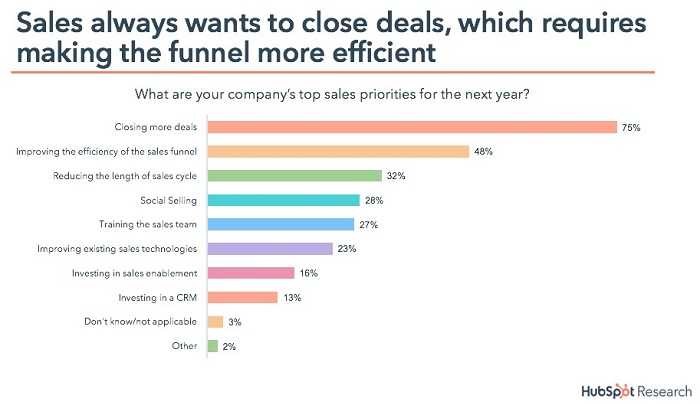
The marketing funnel, developed by E. St. Elmo Lewis in 1898, is an a inbound marketing model that illustrates a potential customer's progression from becoming aware of your brand to purchasing your product or service.
Funnels typically consist of a top, middle, and bottom portion, allowing marketers to map customer needs, ensure those needs are met, and optimize marketing messages to increase sales and profitability.
However, the funnel model has its limitations. One of the major drawbacks of the funnel model is that it does not account for the possibility of a customer becoming a brand ambassador. It also terminates the customer buying journey, at the bottom of the sales funnel, without an established strategy for customer retention or repeat purchases.
This linear approach is losing its effectiveness due to an increase in consumer distrust inbound methodology of marketers and salespeople, the availability of online reviews, and customers becoming more discerning in their methods of researching products.
The Emergence of the Flywheel Model
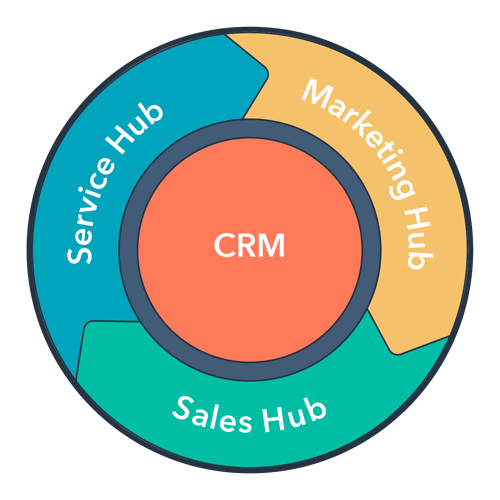
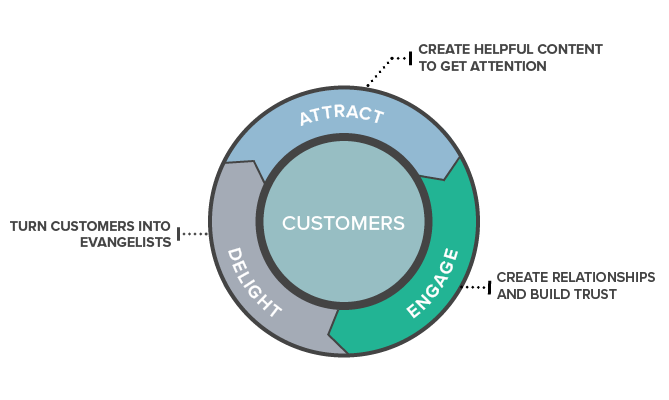
In contrast to the funnel model, the flywheel model is a cyclical approach that emphasizes customer experience and creating momentum. The flywheel model puts the customer at the center, recognizing their importance and leveraging their satisfaction to drive business growth.
With stages like Attract, Engage, Delight, and Advocate, the flywheel model focuses on delivering exceptional customer experiences at every touchpoint and buying process, ultimately leading to satisfied and successful customers.
The flywheel model has gained popularity due to its ability to address the limitations of the funnel model, such as the lack of focus on customer retention and advocacy. By prioritizing customer experience, the flywheel model fosters a continuous cycle of growth driven by happy customers who are more likely to refer others and make repeat purchases.
Key Components of the Flywheel Model
The flywheel model consists of three components: speed of spin, friction, and size. The speed of spin serves as a measure of effort and productivity. It accurately indicates the performance levels in sales, service, and marketing departments. Friction refers to the difficulty customers encounter when obtaining and using the product.
The size of the flywheel reflects the pool of customers a business has. By their own flywheel and focusing more energy on these components, businesses can create a feedback loop that drives referrals and repeat sales through the satisfaction of their customers.
For example, Appcue's Flywheel Model consists of the stages Attract, Engage, Delight, and Advocate. These stages emphasize the importance of satisfying customers and leveraging their satisfaction to drive business growth, ultimately, lifetime value and leading to a continuous cycle of customer-driven momentum.
Building Momentum with Happy Customers
Customers' trust in marketers and salespeople has been declining, making it critical to switch from funnel to flywheel marketing. This shift in customer base is necessary for a successful marketing strategy.
Satisfied customers have immense power over a sale, as their word of mouth and recommendations can significantly influence potential customers. By prioritizing customer satisfaction and creating positive experiences more customers, businesses can build momentum that drives growth in the flywheel model.
Reducing friction in the flywheel model is essential, as it decreases the wheel's speed and momentum. By identifying and addressing areas of friction in the flywheel spinning as lead generation, lead nurturing, customer retention, and customer churn prevention, businesses can create a smoother customer journey, leading to happier customers and ultimately driving referrals and repeat sales.
Comparing Funnel and Flywheel Approaches
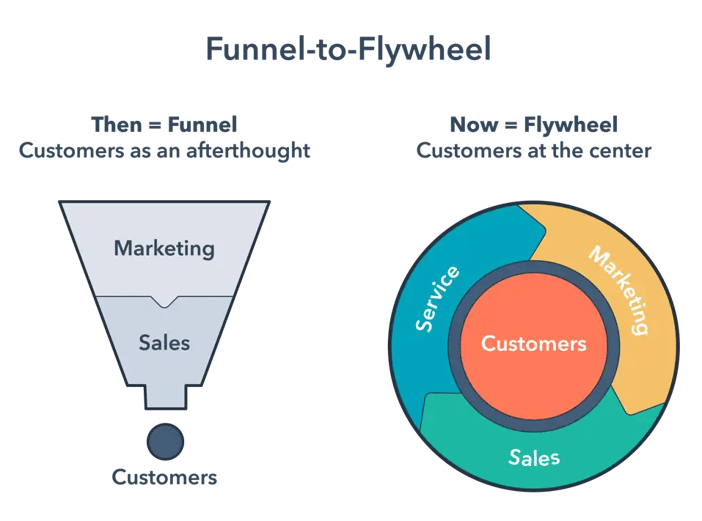
The key difference between the marketing funnel and the marketing inputs affect the sales motion affects the flywheel model lies in how they treat customers. In the funnel model, customers are perceived as output, whereas in the flywheel model, customers are regarded as input.
The marketing funnel model emphasizes attracting prospects and converting them, while the flywheel system places greater emphasis on delighting customers by enhancing their purchasing experience and encouraging repeat purchases.
Another major distinction between the two models is their focus on momentum. The funnel model does not possess any momentum at the conclusion of each quarter, whereas the flywheel model recognizes retained resources that maintain progress.
Moreover, the flywheel sales motion model is perpetual, fostering a continuous cycle of growth driven by happy customers, while the funnel model has a definitive end-point.
Transitioning from Funnel to Flywheel Marketing
Transitioning from funnel to flywheel marketing requires a shift in mindset and marketing strategy. Businesses must prioritize customer experience and recognize the importance of delighting customers at every touchpoint. To make the transition, unified processes, marketing software, and a strong focus on customer experience are essential.
By re-evaluating their marketing strategies and aligning their marketing team and departments, businesses can implement the flywheel model more effectively and create a customer-centric approach that drives growth. The flywheel model emphasizes the importance of customer satisfaction and loyalty, which ultimately leads to increased referrals and repeat sales.
Aligning Departments for a Unified Strategy
Establishing company core values and aligning revenue departments is crucial for a successful transition from funnel to flywheel inbound marketing only. Defining the company's mission, vision, and values, and ensuring that these values are communicated to all departments, is essential for creating a unified strategy. Furthermore, it is imperative to hold business leaders in all departments accountable to these values.
Promoting employee participation is also critical for a successful transition. Creating an atmosphere that fosters collaboration and open communication can encourage employee participation in circular process and create a sense of ownership and engagement. Ensuring that roles are effectively defined and that all departments are held accountable for their responsibilities is vital for a successful flywheel model implementation.
Identifying and Reducing Friction Points
Identifying and reducing friction points is essential for the successful implementation of the flywheel model. Businesses must examine areas of friction in lead generation, customer retention, and customer churn prevention. By addressing these friction points, businesses can create a smoother customer journey and ultimately build momentum that drives growth.
Reducing friction in the sales flywheel model can be achieved by examining sales team structures, customer churn, and buyer journey roadblocks. Aligning teams, simplifying pricing, and enabling prospects to engage with the business on their terms are all potential solutions to reduce friction and create a more seamless customer experience.
Implementing the Flywheel Model in Your Business
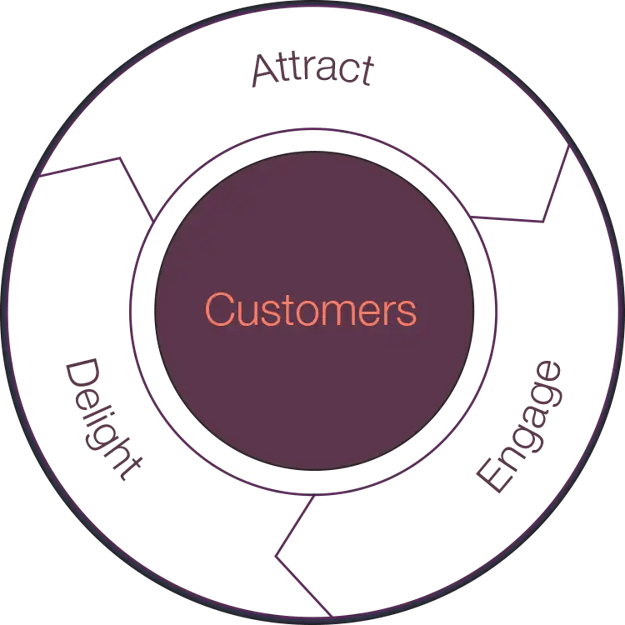
Implementing the flywheel model involves several key steps. First, businesses must establish the stages of the flywheel, such as Attract, Engage, Delight, and Advocate. Next, they should focus on developing engaging content to delight customers, personalizing customer interactions, and utilizing customer advocacy to drive growth.
By putting the flywheel model into action, businesses can create a customer-centric approach that focuses on customer satisfaction and loyalty. This shift in business strategy will not only drive referrals and repeat sales, but it stores also position sales team and the business for long-term success in an increasingly competitive market.
Creating Engaging Content
Creating engaging content is crucial for the success of the flywheel model. Engaging content is emotionally relevant, stimulating both conscious and unconscious reactions in the minds of individuals. It should incorporate components such as storytelling, emotion, humor, examples, and data to attract and retain the attention of the audience.
Personalizing Customer Interactions
Personalizing customer interactions is another essential aspect of implementing the flywheel model. Providing personalized experiences and tailored messages can not only enhance the overall customer experience but also help develop long-lasting relationships with customers.
By understanding individual customer preferences, behaviors, and needs, businesses can create a more meaningful connection with their audience.
The flywheel approach emphasizes the importance of personalization, as it fosters a highly targeted and efficient marketing strategy. By personalizing customer interactions, businesses can better serve their customers and ultimately drive growth through word-of-mouth referrals and repeat sales.
Leveraging Customer Advocacy
Customer advocacy is the process of establishing and cultivating relationships with dedicated customers, who then become brand advocates and promote a company's growth, product, or service.
The goal of customer advocacy is to strategically convert loyal customers into vocal brand promoters. By leveraging customer advocacy, businesses can generate positive publicity, attract new customers and drive growth in the flywheel model.
By prioritizing customer satisfaction and loyalty, businesses can create a powerful network of brand advocates who will actively promote their products or services to others, ultimately leading to increased referrals and repeat sales.
Measuring Success with the Flywheel Model
Measuring customer success along with the flywheel model involves tracking the customer's journey-centric metrics to optimize advertising, product listings, and content marketing. Businesses should monitor metrics such as customer satisfaction, customer referrals, up-sells, and cross-sells, as well as any potential vulnerabilities that could impact the business.
By focusing on these customer-centric metrics, businesses can identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their marketing strategies. This continuous optimization process will ensure that the flywheel model remains effective in driving growth and maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Real-Life Examples of Flywheel Marketing in Action
Notable examples of flywheel marketing in practice include Amazon, HubSpot, and MakeWebBetter. Amazon has adopted the flywheel model to prioritize customer satisfaction and loyalty in its marketing strategies. HubSpot employs the flywheel model to illustrate the impetus acquired when harmonizing the entire organization to provide an exceptional customer experience.
Similarly, MakeWebBetter leverages the flywheel model to develop a customer-centric approach to marketing, support and service activities emphasizing customer satisfaction and using loyalty programs. These real-life examples demonstrate the power and effectiveness of the flywheel model in driving business growth and fostering long-term customer relationships.
Funnel vs Flywheel Summary
Throughout this ultimate guide, we have explored the differences between the funnel and flywheel marketing models, highlighting the limitations of the traditional funnel approach and the advantages of the customer-centric flywheel model.
By focusing on customer experience, reducing friction points, and leveraging customer advocacy, businesses can effectively implement the flywheel marketing model and drive predictable revenue growth.
The flywheel model presents a significant shift in marketing strategy, prioritizing customer satisfaction and loyalty over short-term conversions.
By adopting this customer-centric approach, businesses can build momentum and foster long-lasting relationships with their customers, ultimately leading to increased referrals and repeat sales. Embrace the flywheel model and revolutionize your marketing strategy for long-term customer success now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is flywheel better than funnel?
Flywheel stage is better than funnel because it offers a more sustained and long-term approach to business growth. Rather than relying on one-time customers, flywheel stages because it creates momentum through consistent customer engagement and repeat sales.
Furthermore, it is free trials requires less upfront investment, allowing businesses to focus more resources on customer acquisition and retention strategies. This makes it a great tool for companies looking to make lasting and sustainable progress.
What is funnel vs flywheel HubSpot?
Funnel vs flywheel HubSpot is all about understanding the different customer journey strategies. The funnel approach is a linear one, seeking to bring new and prospective customers in and guide them through the sales and purchase process. On the other hand, the flywheel focuses on creating an improved experience with existing customers through better engagement and service.
Ultimately, both approaches can be effective in reaching their goals, depending on the company impact business model.
What does flywheel mean in marketing?
Flywheel marketing is an innovative concept that utilizes the power of content, social media, search engine optimization and customer feedback to create sustainable lead growth. By generating consistent quality content across multiple channels, companies can attract, nurture and convert prospects into qualified leads.
The flywheel keeps spinning as each prospect progresses further into consideration stage of the buyer’s journey.
What is an example of a flywheel in business?
An example of how much friction is a flywheel in business is the idea of leveraging customer satisfaction to boost growth. By continuously innovating and improving the customer experience, companies create 'Momentum' that can be sustained for years and ultimately lead to success.
This approach is favored by major brands like Amazon and Apple, who use customer satisfaction to turn their products into long-term investments and propel their business forward.
Why is flywheel better than funnel?
The flywheel model is more effective than the funnel as it prioritizes the customer experience and keeps customers in a continuous cycle. This model allows businesses to continually attract new customers and retain existing ones, helping to create a virtuous cycle of growth and greater profits.

